RSA Algorithm
- Rivest-Shamir-Aldeman Algorithm
- an asymmetric cryptography algorithm utilizes public and private generated from large prime numbers used to encrypt and decrypt data.
The public key consists of two numbers where one number is a multiplication of two prime numbers. The private key is also derived from the same two prime numbers meaning if the public key primes are compromised, then so is the private key.
- Φ
- Φ(Phi) counts the number of numbers that are less than or equal to n and only share the factor of 1 with n
Geeks for Geeks example:
Geek For Geeks: RSA Algorithm Cryptography
Generating Public Key:
Select two prime no's. Suppose P = 53 and Q = 59.
Now First part of the Public key : n = P*Q = 3127.
We also need a small exponent say e :
But e Must be
An integer.
Not be a factor of Φ(n).
1 < e < Φ(n),
Let us now consider it to be equal to 3.
Our Public Key is made of n and e
Generating Private Key:
We need to calculate Φ(n) :
Such that Φ(n) = (P-1)(Q-1)
so, Φ(n) = 3016
Now calculate Private Key, d :
d = (k*Φ(n) + 1) / e for some integer k
For k = 2, value of d is 2011.
Primality Testing
- Primality Testing
- Testing for values to prove whether a number $n$ is prime.
Input: $n ∈ Z+ > 1$ Output: Boolean output indicating if $n$ is Prime or Composite
Brute Force Algorithm
There is no efficient algorithm known so far that can efficiently find prime factors without Brute Force
Brute Force Algorithm:
Input: Integer N greater than 1.
Output: "Prime" if N is prime, else "Composite" if N is composite.
For x = 2 to N-1
If x evenly divides N,
Return( "Composite" )
End-for
Return( "Prime" )
However, we can make our algorithm slightly better by instead searching for all values from 2 to √n since its been proven that composite numbers must have a prime factor equal to or less that √n. See Prime Composite Numbers: Trial Division Theorem
Improved Brute Force Algorithm:
Input: Integer N greater than 1.
Output: "Composite" if composite, else "Prime".
For x = 2 to √n
If x evenly divides N,
Return( "Composite" )
End-for
Return( "Prime" )
The Prime Number Theorem
Let π(x) be the number of prime numbers from range 2 to x. Then:
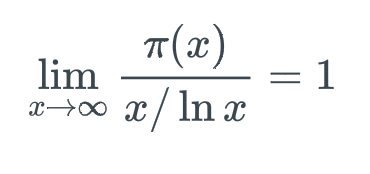
See Prime Number Approximation: