Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a process that optimizes the output of LLMs do that it utilizes and references a specific knowledge or domain base that may not have been included in the LLM’s training data. RAG can be seen as a cost-efficient extension of the LLM’s abilities using an organization’s knowledge base while improving the outputs so that it remains relevant, accurate, and useful in various contexts without needing to retrain the LLMs. RAG will redirect the LLM to retrieve information that has the pre-determined authority so that organizations can have greater control over the generative outputs and so that users may have greater insight into how responses were generated.
Disadvantaged of LLMs
- Hallucination or presenting false information when it doesn’t have the answer
- Presenting out of date information which may not be useful or may even be incorrect
- Presenting generic when users expect a more specific response
- Generating a response from unreliable sources used to train the model
- Presenting irrelevant or inaccurate responses due to terminology or context confusion
Benefits to RAG Models
- Cost-effective: Orgs don’t have to retrain foundation models for specific information which is highly expensive
- Current information: Developers can provide the latest research, documentation, statistics, or news.
- Enhanced user trust: RAG allows LLMs to present information with source attribution to include citations or references to sources.
- More control: Developers can control access to information to best suit the target audience or restrict information to different authorization levels.
- Iterative and testable: Developers can test and iterate on responses by troubleshooting with the amount or quality of information referenced by the LLM.
How does RAG work
Steps:
- Create external data
- Retrieve relevant information
- Augment the LLM prompt
- Update external data
Create External Data
Any data outside of the LLMs original training dataset is called external data. External data can come from various sources such as APIs, databases, documentation, or other resources and can be in various formats such as files, records, or text. Organizations create and convert external data to store numerical representations of their data in vector databases. This will create a knowledge library that generative AI models can understand and utilize in their responses.
Information Retrieval
A relevancy search is conducted by converting user queries into vector representations to then match against the vector databases. After finding relevant documents and domains that match the user query, a relevancy score will be calculated using the vector calculations and representations. The system will be able to pull the most highly relevant information relating the user query input.
LLM Prompt Augmentation
Using the retrieved information, the RAG model will then augment the LLM query with relevant information data. Using prompt engineering techniques, relevant information and data will be added into the LLM’s context so that it can generate accurate and relevant responses.
Updating & Maintaining External Data
It is important that organizations continue to update and maintain their external data for accuracy, timeliness, and relevancy to prevent the data and generative responses from being stale. Using automated real time processes or periodic batch processing, the external data store can be updated with new information that improves responses. Alternatively, organizations can reevaluate their data analytics/data science approaches to better suit their business needs.
Conceptual Diagram
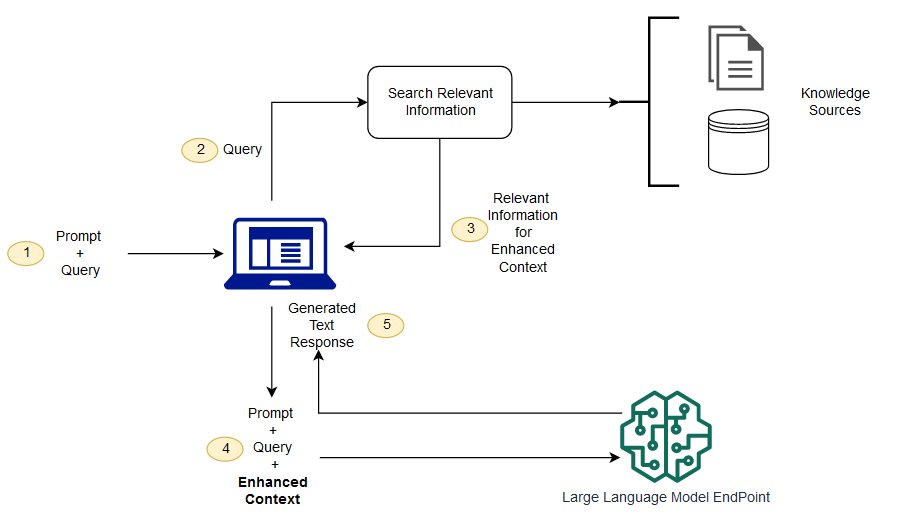 Source: AWS
Source: AWS
This is an example conceptual diagram that highlights a potential workflow for using RAG with LLMs. It is not the only way to implement RAG; another example implementation may instead send a request to a backend service which then makes a request to a LLM endpoint before the user receives any response.